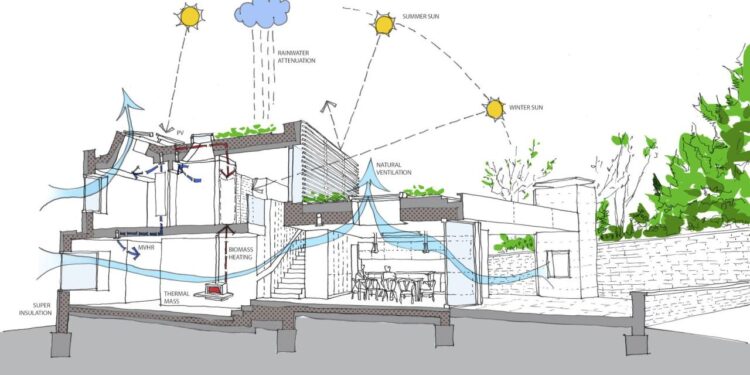
Climate change stands as one of the most pressing issues of our era, affecting ecosystems, economies, and communities globally. The architectural industry holds a pivotal role in crafting solutions to mitigate and adapt to these environmental changes.
Mojok.co team explores how innovative architectural designs can address climate change by reducing carbon emissions, enhancing energy efficiency, and promoting sustainable living practices.
The Imperative Role of Sustainable Architecture
Architecture transcends mere aesthetic appeal; it embodies the responsibility of designing buildings that are environmentally conscious and resource-efficient throughout their lifecycle. Sustainable architecture aims to minimize the negative environmental impact of buildings by enhancing efficiency and moderation in the use of materials, energy, and development space.
Embracing Sustainable Building Materials
Selecting eco-friendly materials is crucial in reducing the environmental footprint of construction projects. Sustainable materials contribute to energy conservation and waste reduction.
A. Recycled and Reclaimed Materials
Utilizing recycled steel, glass, and reclaimed wood decreases the demand for new raw materials, conserving resources and lowering greenhouse gas emissions associated with production.
B. Locally Sourced Materials
Procuring materials from local suppliers reduces transportation emissions and supports regional economies, fostering community resilience.
C. Rapidly Renewable Resources
Materials such as bamboo, cork, and straw bale are rapidly renewable and have a lower environmental impact compared to traditional building materials.
Designing for Energy Efficiency
Energy-efficient building designs are essential in reducing the operational carbon footprint of structures.
A. Passive Solar Design
Incorporating passive solar principles allows buildings to naturally regulate temperature by maximizing solar heat gain in winter and minimizing it in summer.
B. Advanced Insulation Techniques
High-performance insulation materials reduce the need for artificial heating and cooling, leading to significant energy savings.
C. Energy-Efficient Lighting and Appliances
Integrating LED lighting and Energy Star-rated appliances decreases electricity consumption and operational costs.
Integration of Renewable Energy Systems
Incorporating renewable energy technologies into building designs reduces reliance on fossil fuels.
A. Photovoltaic Solar Panels
Installing solar panels converts sunlight into electricity, providing a clean and renewable energy source for the building.
B. Wind Energy Solutions
In areas with sufficient wind resources, small-scale wind turbines can supplement energy needs and contribute to sustainability goals.
C. Geothermal Heating and Cooling
Geothermal systems leverage stable underground temperatures to efficiently heat and cool buildings, reducing energy consumption.
Green Roofs and Vertical Gardens
Green roofs and walls enhance urban biodiversity and contribute to environmental sustainability.
A. Enhanced Insulation
Vegetative layers provide additional insulation, reducing energy required for heating and cooling.
B. Urban Heat Island Mitigation
Plants absorb sunlight and reduce surface temperatures, combating the urban heat island effect.
C. Stormwater Management
Green roofs absorb rainwater, decreasing runoff and reducing the burden on municipal drainage systems.
Water Conservation Strategies
Efficient water use is a critical component of sustainable building design.
A. Rainwater Harvesting Systems
Collecting and storing rainwater for non-potable uses conserves municipal water supplies and reduces utility costs.
B. Greywater Recycling
Treating and reusing greywater from sinks and showers for irrigation minimizes freshwater consumption.
C. Low-Flow Plumbing Fixtures
Installing low-flow toilets, faucets, and showerheads significantly reduces water usage without compromising performance.
Adaptive Reuse and Renovation
Repurposing existing structures is an environmentally friendly alternative to new construction.
A. Preservation of Historical Buildings
Restoring historic buildings maintains cultural heritage and reduces the environmental impact associated with demolition and new construction.
B. Conversion Projects
Transforming obsolete buildings into functional spaces revitalizes communities and maximizes the use of existing resources.
C. Material Reclamation
Salvaging materials from deconstructed buildings minimizes waste and reduces the demand for new materials.
Sustainable Urban Planning
Architects contribute to designing cities that are resilient and sustainable.
A. Compact City Design
Promoting higher-density developments reduces land consumption and encourages efficient public transportation systems.
B. Green Spaces and Parks
Integrating parks and greenways enhances biodiversity and provides recreational areas for residents.
C. Sustainable Transportation Infrastructure
Designing infrastructure that supports biking, walking, and public transit reduces carbon emissions from vehicles.
Compliance with Green Building Standards
Adhering to recognized green building standards ensures environmental performance and sustainability.
A. LEED Certification
The Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED) certification provides a globally recognized framework for environmentally responsible buildings.
B. BREEAM Assessment
The Building Research Establishment Environmental Assessment Method (BREEAM) evaluates the sustainability performance of buildings.
C. Energy Star Ratings
Energy Star certifications identify buildings that meet strict energy efficiency guidelines set by government agencies.
Technological Innovations Driving Sustainability
Advancements in technology offer new opportunities for sustainable architecture.
A. Smart Building Technologies
Automated systems manage energy use, lighting, and climate control, optimizing efficiency based on occupancy and usage patterns.
B. Building Information Modeling (BIM)
BIM software enhances collaboration and efficiency in the design and construction process, reducing errors and material waste.
C. Advanced Materials
Development of materials like aerogels and phase-change materials improves insulation and energy storage capabilities.
Community Engagement and Education
Educating communities about sustainable practices fosters widespread adoption of green architecture.
A. Workshops and Seminars
Hosting educational events raises awareness about the benefits of sustainable building practices.
B. Collaborative Design Processes
Involving community members in the design process ensures that buildings meet local needs and encourage community stewardship.
C. Educational Institutions
Incorporating sustainability into educational curricula prepares future generations to prioritize environmental considerations.
Addressing Challenges and Barriers
Overcoming obstacles is essential to advance sustainable architectural solutions.
A. Economic Considerations
While initial costs may be higher, sustainable designs often result in long-term savings through reduced operational costs.
B. Regulatory Hurdles
Advocating for supportive policies and incentives can facilitate the adoption of green building practices.
C. Cultural Shifts
Promoting the value of sustainability encourages acceptance and demand for eco-friendly designs.
The Future of Sustainable Architecture
The ongoing evolution of architectural practices points toward a more sustainable future.
A. Net-Zero Energy Buildings
Designing buildings that produce as much energy as they consume minimizes environmental impact.
B. Biophilic Design
Incorporating natural elements into building design enhances occupant well-being and environmental performance.
C. Circular Economy Principles
Emphasizing reuse and recycling in construction reduces waste and conserves resources.
Conclusion
Architectural solutions are integral to combating climate change. By embracing sustainable materials, energy-efficient designs, renewable energy integration, and innovative technologies, the architectural industry can significantly reduce environmental impact. Mojok.co team believes that through collaboration, education, and commitment to sustainability, architects can lead the way toward a resilient and eco-friendly future for all.